AUTOSOMAL RECESSIVE
The phenotype is usually observed only in homozygotes because of the recessive nature of the gene in a single dose. Fig 29. The typical pedigree shows normal parents and some normal offspring with affected siblings among them. Fig. 30. This condition is suspected when the parents are consanguineous and they have for example half-normal levels of enzyme, while the affected have low or absent levels.

Fig 29
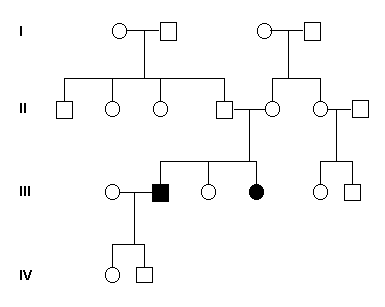
Fig 30
CRITERIA
- If the trait is rare, parents, relatives and other siblings are usually normal.
- If the recessive genes are alleles, all children of two affected parents are affected.
- If two normal heterozygotes mate, the segregation frequency for each pregnancy is 25% affected, 50% heterozygous carriers and 25% homozygous normal.
- Both sexes are equally affected.
- Parental consanguinity increases the incidence.
SPECIAL FEATURES
- Carrier states are usually normal but may show half-normal enzyme levels as seen with hexosaminidase A levels in Tay - Sachs disease.
- Siblings or brothers and sisters have half their genes in common and first cousins (having the same set of grandparents) have one - eighth of their genes in common. Consanguinity therefore increases the chances of the birth of affected homozygotes. It is therefore involved in counseling of religious and geographic isolates.
- Certain racial groups may carry the recessive gene at
a higher frequency, and these populations may need screening programmes
to identify the heterozygous carriers who can then be prevented from mating
with each other. Examples are :
Sickle cell anaemia in blacks
Tay - Sachs disease in Ashkenazi Jews
Cystic fibrosis in Northern European Caucasians - Certain heterozygotes (carriers) in conditions like Sickle cell disease may, under conditions of reduced oxygen tension like exercise at high altitude, parachuting, travel in an unpressurised aircraft at a high altitude or just before anaesthesia show the cells "sickling" in vivo (inside the body) and manifest symptoms as in a homozygote. These carriers are said to have the sickle cell trait.
CLINICAL EXAMPLES
- Galactosaemia occurs due to the absence of an enzyme galactose - 1 - phosphate uridyl transferase and the inability to use lactose. Patients have mental deficiency, cataract, hepatomegaly and may die of sepsis.
- Homocystinuria is due to increased levels of homocystine and methionine following the deficiency of cystathionine beta synthetase which normally converts homocysteine to cystathionine. Abnormal body proportions, dislocated lenses, mental handicap and mental problems are seen.
- Cystic fibrosis has its gene located on the short arm of chromosome 7 (7p). Affected infants present with failure to thrive, chronic respiratory infections and malabsorption. Secretions of the gut and lungs are thick and sweat is altered with high sodium and chloride. This condition has the potential for prenatal diagnosis and screening using DNA studies.
- Sickle cell anaemia is produced by the homozygous status of two mutant beta-globin polypeptide genes on chromosome 11, each producing a defective beta-globin polypeptide chain. The change in each of these new chains is the substitution of the amino acid glutamic acid with a valine at position 6 from the amino end, producing HbS instead of HbA. This causes distortion(sickle shape) of red blood cells. The homozygous normal will be HbA / HbA, while the trait would be HbA / HbS and the disease state HbS / HbS.
- Thalassemias are of two types, Alpha and Beta thalassemias. In the Alpha variety one or two or three or all four of the Alpha-globin genes on chromosome 16, responsible for the four Alpha globin chains in HbA may be deleted in stages. The stages and features are shown.
- Phenylketonuria Refer page 41, section 1b.
GENOTYPE CLINICAL STATE
( A A / A A) NORMAL
( A A / A - ) * Alpha thalassemia type 2 hetero.
ASYMPTOMATIC
( A A / - - ) * Alpha thalassemia type 1 hetero.
( A - / A - ) Alpha thalassemia type 2 homo.
ASYMPTOMATIC
( A - / - - ) Haemoglobin H Disease CHRONIC HAEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA
( - - / - - ) ** Alpha thalassemia type 1 homo.
HYDROPS FOETALIS - DEATH IN UTERO
EARLY NEONATAL DEATH
* carrier detection
** prenatal diagnosis by DNA analysis
In the Beta variety, the two genes for the two Beta globin chains are on each of the short arms of chromosome 11. The deletion of one produces the heterozygote with mild microcytic, hypochromic anaemia with target cells with raised Hb A2 and a slight increase of Hb F. A deletion of both genes produces the homozygote with severe hypochromia, microcytosis, target cells, increased Hb F and Hb A2 and haemolysis. Beta globin synthesis is reduced or absent with a reduced life span. Carrier detection and prenatal diagnosis are possible.
GENOTYPE CLINICAL STATE
( B / B) NORMAL
( B / - ) Carrier
MILD ANAEMIA
( - / - ) Affected
SEVERE ANAEMIA